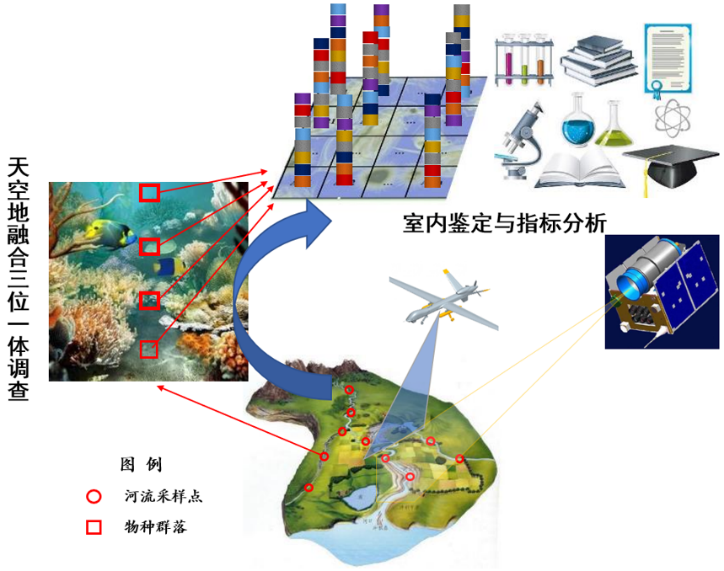
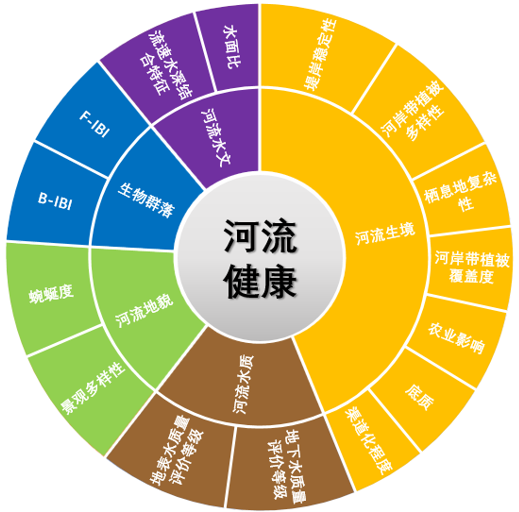
生物-环境互馈机理
近年来我国大力开展水生态保护与环境综合治理,水生态文明城市建设进展顺利,水生态环境较以往有了较大改善,但由于栖息地环境因子与生物群落的影响与反馈机理研究较少,河流湖库生态系统的组成结构及健康状况缺乏全面了解和有效评估,导致水生态文明城市建设效果难以定量跟踪评估,区域水生态系统健康状况改善效果有限。为此,团队2014-2016年与济南市水文局合作,在济南市选择具有代表性的站点,逐年分春、夏、秋三季开展了覆盖全济南市水域的大规模水量-水质-水生态同步监测采样,瞄准生产实际问题,进行产学研有效结合,开展了生物群落演化驱动因子识别、环境因子对水生态食物网影响、生态修复效果评估模型构建、人类活动对生态系统影响、气候变化背景下未来河流健康预测等方面开展了一系列研究,为我国水生态修复提供了理论与模型工具,支撑我国水生态文明建设方略持续推进。
【成果分享】
[1] Zhao, C., Pan, T., Dou, T., Liu, J., Liu, C., Ge, Y., Zhang, Y., Yu, X., Mitrovic, S. and Lim, R., 2019. Making global river ecosystem health assessments objective, quantitative and comparable. Science of The Total Environment. 667: 500-510. (DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.379)
[2] Zhao, C., Zhang, Y., Yang, S., Xiang, H., Sun, Y., Yang, Z., Yu, Q. and Lim, R.P. (2018). Quantifying effects of hydrological and water quality disturbances on fish with food-web modeling. Journal of Hydrology, 560: 1-10. (DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.03.017)
[3] Zhao, C.S., Shao, N.F., Yang, S.T., Xiang, H., Lou, H.Z., Sun, Y., Yang, Z.Y., Zhang, Y., Yu, X.Y., Zhang, C.B., & Yu, Q. (2018). Identifying the principal driving factors of water ecosystem dependence and the corresponding indicator species in a Pilot City, China.Journal of Hydrology, 556 :488–499. (DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.11.031)
[4] Zhao, C.S., Yang, S.T., Xiang, H., Liu, C.M., Zhang, H.T., Yang, Z.L., Zhang ,Y., Sun, Y., Mitrovic, S.M., & Yu, Q. (2015). Hydrologic and water-quality rehabilitation of environments for suitable fish habitat. Journal of Hydrology, 530, 799-814. (DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.10.031)
[5] Zhao, C.S., Yang, S.T., Liu, C.M., Dou, T.W., Yang, Z.L., Yang, Z.Y., Liu, X.L., Xiang, H., Nie, S.Y., &Zhang, J.L. (2015). Linking hydrologic, physical and chemical habitat environments for the potential assessment of fish community rehabilitation in a developing city. Journal of Hydrology, 523: 384-397. (DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.01.067)
[6] Zhao, C.S., Liu, C.M., Xia, J., Zhang, Y.Y., Yu, Q., & Eamus, D. (2012). Recognition of Key Regions for Restoration of Phytoplankton Communities in the Huai River basin, China. Journal of Hydrology, 420-421: 292-300. (DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.12.016)
[7] Zhao, C.S., Shao, N.F., Yang, S.T., Ren, H., Ge, Y.R., Zhang, Z.S., Feng, P. and Liu, W.L., 2019. Quantitative assessment of the effects of human activities on phytoplankton communities in lakes and reservoirs. Science of The Total Environment. 665: 213-225. (DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.117)
[8] Zhao, C.S., Yang, Y., Yang, S.T., Xiang, H., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z.Y., Chen, X. and Mitrovic, S.M. (2019). Predicting future river health in a minimally influenced mountainous area under climate change. Science of The Total Environment. 656: 1373-1385. (DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.430)
[9] Zhao, C.S., Shao, N.F., Yang, S.T., Ren, H., Ge, Y.R., Feng, P., Dong, B.E. and Zhao, Y., 2019. Predicting cyanobacteria bloom occurrence in lakes and reservoirs before blooms occur. Science of The Total Environment. 670: 837-848. (DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.161)